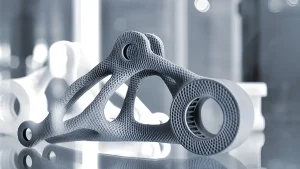
Material choice is fundamental in 3D printing, influencing the final product’s strength, flexibility, and durability. Different materials cater to diverse applications, from prototyping to functional components, and understanding their characteristics helps in making informed decisions.
Commonly Used Materials in 3D Printing
Plastics/Polymers:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): A popular choice for beginners, PLA is easy to print and biodegradable. Ideal for prototyping and educational projects, it offers a smooth finish and vibrant colors.?
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Known for its toughness and impact resistance, ABS is suitable for functional parts. However, it requires a heated bed and proper ventilation due to its tendency to emit fumes.?
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG combines the best of PLA and ABS, offering durability and flexibility. It’s perfect for parts that need to withstand stress and environmental conditions.?
- Nylon: Renowned for its strength and flexibility, Nylon is used in engineering and mechanical applications where parts need to endure stress and wear.?
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is highly flexible and abrasion-resistant, making it ideal for creating parts that require elasticity, like phone cases and gaskets.?
Metals:
- Stainless Steel: Commonly used in industrial settings for its strength and corrosion resistance. It’s ideal for durable parts and tooling.?
- Titanium: Lightweight and biocompatible, Titanium is used in aerospace and medical implants. It’s known for its strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion.?
- Aluminum: Favored in aerospace and automotive industries, Aluminum offers a good balance of strength and lightweight properties.?
- Cobalt-Chrome: Used in medical applications for its high strength and wear resistance, making it suitable for prosthetics and dental implants.?
Resins:
- Standard Resins: Provide high detail and smooth finishes for prototypes and intricate designs.?
- Tough Resins: Designed for engineering applications where durability and impact resistance are crucial.?
- Flexible Resins: Allow for the creation of parts that need to bend and stretch, such as wearable devices.?
- Dental and Medical Resins: Specialized for producing dental models and medical devices, with properties tailored to these fields.?
Composites:
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers: Offer high strength and low weight, used in aerospace and automotive industries for performance parts.?
- Glass-Filled or Wood-Filled Plastics: These composites enhance aesthetic appeal and mechanical properties, used in consumer products and decorative items.?
Specialty Materials:
- Conductive Filaments: Enable the printing of electronic components and circuits, merging 3D printing with electronics.?
- Water-Soluble Filaments: Simplify the removal of support structures in complex prints, reducing post-processing time.?
- Biocompatible Materials: Essential for medical applications, these materials ensure compatibility with human tissues.?
Comparing Different Materials
Each material comes with its strengths and weaknesses. For instance, PLA is user-friendly but lacks the strength of ABS. Metals like Titanium offer exceptional properties but come at a higher cost. Understanding these trade-offs helps in selecting the right material for your project.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
When selecting a material, consider the project’s specific needs, including application requirements, environmental factors, and post-processing needs. For example, if you’re creating a part that will be exposed to high temperatures, materials like PETG or certain metals would be more appropriate.
Future Trends in 3D Printing Materials
Emerging trends include biodegradable plastics and smart materials that can change properties in response to external stimuli. Sustainability is also a growing focus, with efforts to reduce the environmental impact of 3D printing materials.
Choosing the right 3D printing material is crucial for achieving the desired outcome in your projects. Whether you’re prototyping a new design or creating functional parts, understanding the material properties helps in making informed choices. Explore the endless possibilities and keep learning about new materials to stay ahead in the world of 3D printing.
Discover more about 3D printing materials on our website or contact Raymankind for expert advice on selecting the perfect material for your needs.?